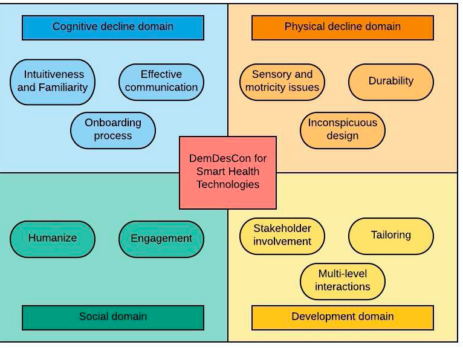
We explored the factors that influence the adoption of smart health technologies by people with dementia and their informal caregivers. Through a scoping review of 109 studies, we identified key barriers and facilitators, ranging from design challenges to ethical concerns. Based on these insights, we proposed the DemDesCon framework, which outlines essential design considerations for creating effective s-Health solutions for this population.
What was the context of our study?
Dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative condition affecting millions globally, with numbers expected to rise sharply in coming decades. Informal caregivers often bear the brunt of care responsibilities, which can lead to significant stress and burden. Smart health technologies hold promise for easing caregiving and enhancing the quality of life for people with dementia. However, their adoption has been inconsistent, largely due to usability issues, ethical concerns, and a lack of user-centric design principles.
What did we do?
We conducted a scoping review following the Arksey and O’Malley methodology to synthesize existing literature on the adoption of s-Health technologies for people with dementia and their informal caregivers. Our search covered databases like PubMed, Cochrane Library, IEEE, and Scopus. From 2373 publications, we included 109 studies that met our criteria, focusing on usability, user experience, adoption barriers, and satisfaction levels. The data were thematically analyzed to identify key factors influencing technology adoption.
What did we find?
The review revealed five major themes affecting the adoption of s-Health technologies:
- Attitudinal Aspects: Positive attitudes toward technology (e.g., improved quality of life) facilitated adoption, while negative attitudes (e.g., frustration or mismatch of expectations) hindered it.
- Ethical Concerns: Privacy and autonomy concerns were significant barriers, particularly around monitoring and data ownership.
- Technology-Related Challenges: Issues such as poor design, low digital literacy, and unclear usefulness often led to rejection.
- Condition-Related Challenges: Cognitive and physical decline in PwD created unique barriers, requiring tailored and adaptive solutions.
- Gaps in Knowledge: A lack of market-specific research and practical design guidelines was evident, limiting the effectiveness of available solutions.
We synthesized these findings into the DemDesCon framework, which highlights considerations for cognitive decline, physical decline, social interaction, and stakeholder involvement in designing s-Health technologies.
Why is this important?
This work underscores the importance of user-centered design in creating effective s-Health technologies for PwD and their caregivers. The DemDesCon framework serves as a practical guide for developers, researchers, and policymakers to address the specific needs of this population. By emphasizing inclusivity, adaptability, and ethical considerations, these technologies can achieve better adoption and integration into daily care routines, ultimately improving the lives of both PwD and their caregivers.
Reference
Guisado-Fernández E, Giunti G, Mackey LM, Blake C, Caulfield BM. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Smart Health Technologies for People With Dementia and Their Informal Caregivers: Scoping Review and Design Framework. JMIR Aging. 2019;2(1):e12192. https://doi.org/10.2196/12192.